Deployments
Deployments in MetaKraftwerk provide a comprehensive framework for automating the distribution and execution of build results across different environments and platforms. The deployment system enables seamless transfer of generated files and objects from MetaKraftwerk to target systems, ensuring consistent and reliable deployment processes across various data integration technologies.
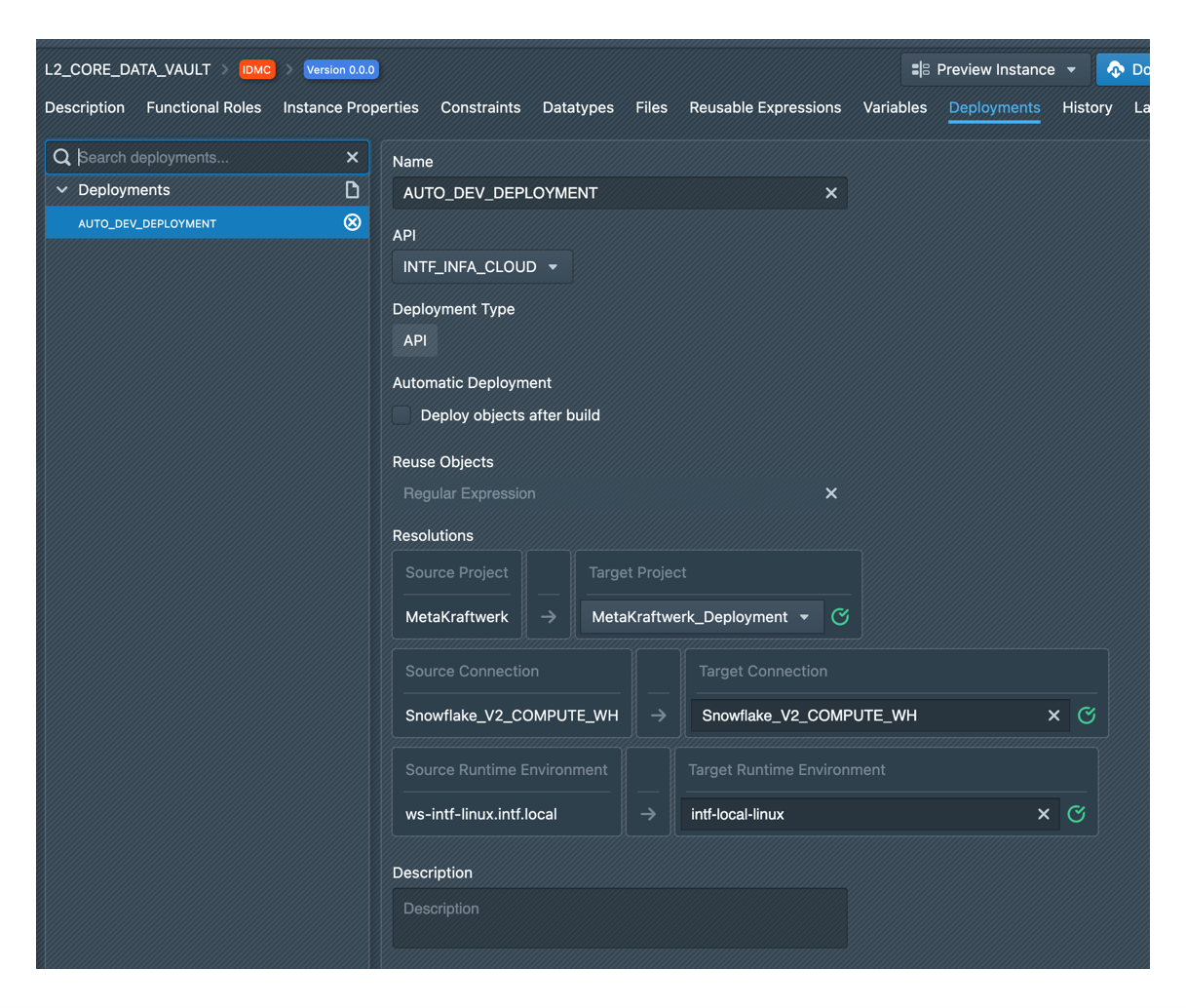
A deployment in MetaKraftwerk is defined within the pattern configuration and specifies which created files from build operations are deployed to which target environment. The deployment definition determines how build results are automatically distributed to configured target systems through selected APIs and connections.
Core Concepts
Deployment Definition
A deployment is defined within the pattern configuration and specifies:
- Target Environment: The destination platform or system for build results
- API/Connection Selection: The specific API or connection used for deployment operations
- File Mapping: Which created files are deployed to which target locations
- Object Handling: Configuration for existing objects (retain/overwrite policies)
- Automation Settings: Automatic execution parameters following build completion
Build Result Deployment
Deployments in MetaKraftwerk are specifically designed to handle build results - the files and objects generated during the build process. When a build completes successfully, the deployment system automatically processes the generated artifacts according to the defined deployment configurations.
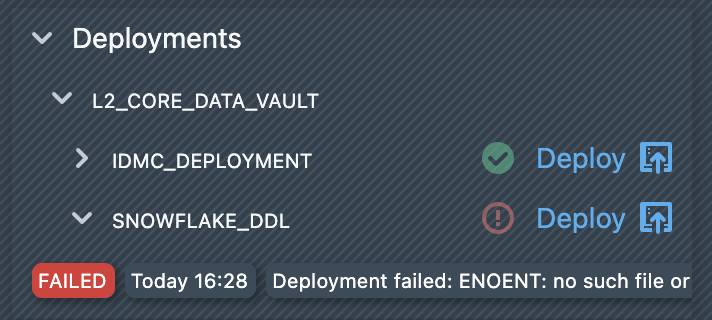
If you have disabled automatic deployments, you could manually start a deployment. To do this, you must first open a build. Under ‘Deployments,’ you will see a list of all available deployments. Clicking on ‘Deploy’ starts the deployment and the generated objects are deployed to the target system using the deployment configuration. The result of the deployment is displayed directly below the deployment in the list. A deployment can be completed with either the status FINISHED or FAILED. If the deployment fails, an error message will be displayed next to the deployment entry.
API and Connection-Based Architecture
Each deployment must specify an API or connection that will be used for the deployment operation. The selected connection type determines:
- Available Configuration Options: Different connection types provide different deployment settings
- Object Handling Policies: How existing objects in the target environment are managed
- Authentication and Security: Connection-specific security and authentication requirements
- Target System Integration: Platform-specific integration capabilities and limitations
Automatic Deployment
MetaKraftwerk supports automatic deployment functionality through the "Deploy objects after build" option. When enabled, this feature automatically triggers deployment processes immediately following successful build operations, ensuring seamless integration between development and deployment phases.
Agent-Based Deployment
Many deployment types utilize agent-based architecture where deployment agents handle the actual transfer and execution of objects on target systems. This approach provides:
- Distributed Processing: Agents can be deployed close to target systems
- Secure Communication: Encrypted communication channels between MetaKraftwerk and agents
- Environment Context: Agents can make use of environment variables which you define on the system where the agent runs
Deployment Types
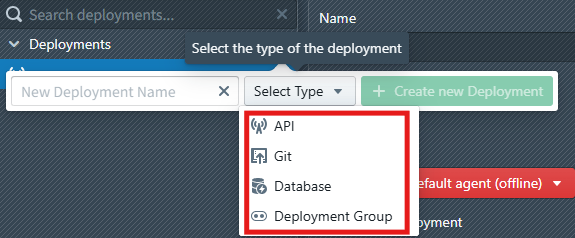
MetaKraftwerk supports four main deployment types, each optimized for specific target platforms and use cases:
| Deployment Type | Description |
|---|---|
| API | A deployment against a target API (e.g. IDMC or Fabric) |
| Database | Used to deploy database objects or procedures to a database |
| Git | Deploys generated artefacts/files to a Git repository |
| Group | Can be used to group various other deployments and execute them sequentially or in parallel |
Creating Deployments
Pattern-Based Deployment Configuration
Deployments are defined within the pattern configuration, creating a direct relationship between patterns and their target deployment environments. This approach ensures that each pattern can have customized deployment strategies appropriate for its specific requirements.
Step 1: Access Pattern Configuration
- Navigate to the pattern where you want to configure deployments
- Access the pattern's deployment configuration section (click on 'Deployments' in the tab list)
- Review existing deployments or create new deployment definitions
Step 2: Define Deployment Specifications
The deployment definition process involves specifying:
- API/Connection Configuration: Select the appropriate API or connection for deployment operations
- Build Result Mapping: Identify which files created during the build process should be deployed
- Target Environment Selection: Choose the destination environment for the build results
API/Connection Selection Process
Step 1: Choose Deployment API/Connection
Select from available APIs and connections based on your target environment:
- Database Connections: For direct database deployments
- Cloud APIs: For cloud platform deployments (IDMC, Synapse, etc.)
- Version Control APIs: For Git repository deployments
- ETL Platform APIs: For PowerCenter, Informatica, or other ETL tools
Step 2: Configure Connection-Specific Settings
Depending on the selected connection type, configure additional parameters:
Object Handling Policies:
- Retain: Preserve existing objects in target environment
- Overwrite: Replace existing objects with new build results
- Merge: Combine existing objects with new deployments
- Version: Create versioned deployments maintaining object history
Environment-Specific Configuration:
- Target folder or schema specifications
- Security and authentication parameters
- Performance and resource allocation settings
- Error handling and rollback procedures
Automatic Deployment Configuration
Enable Automatic Deployment: Deployments can be configured for automatic execution immediately following successful build operations:
- Activation: Enable "Deploy objects after build" option in deployment configuration
- Trigger Conditions: Define conditions that must be met for automatic deployment
- Build Integration: Automatic deployment triggers only after successful build completion
- Error Handling: Configure behavior when automatic deployment encounters errors
Benefits of Automatic Deployment:
- Immediate Distribution: Build results are immediately available in target environments
- Reduced Manual Effort: Eliminates manual deployment steps from development workflow
- Consistency: Ensures all successful builds are consistently deployed
- Integration: Seamless integration between development and deployment phases
Integration with Release Management
Deployments work seamlessly with MetaKraftwerk's Release Management system:
Release-Specific Deployments
- Release Context: Deployments operate within specific release contexts
- Version Control: Automatic version control integration with release states
- Branch Management: Support for release-specific branching strategies
- Merge Operations: Coordinated deployment of merged changes
Automated Workflows
- Build Integration: Automatic deployment triggers following successful builds
- Release Pipelines: Integration with release promotion pipelines
- Quality Gates: Deployment gates based on quality and validation criteria
- Approval Workflows: Integration with approval and governance processes